Technologies & ingredients for effective sun protection
FAQs
What is broad-spectrum sunscreen?
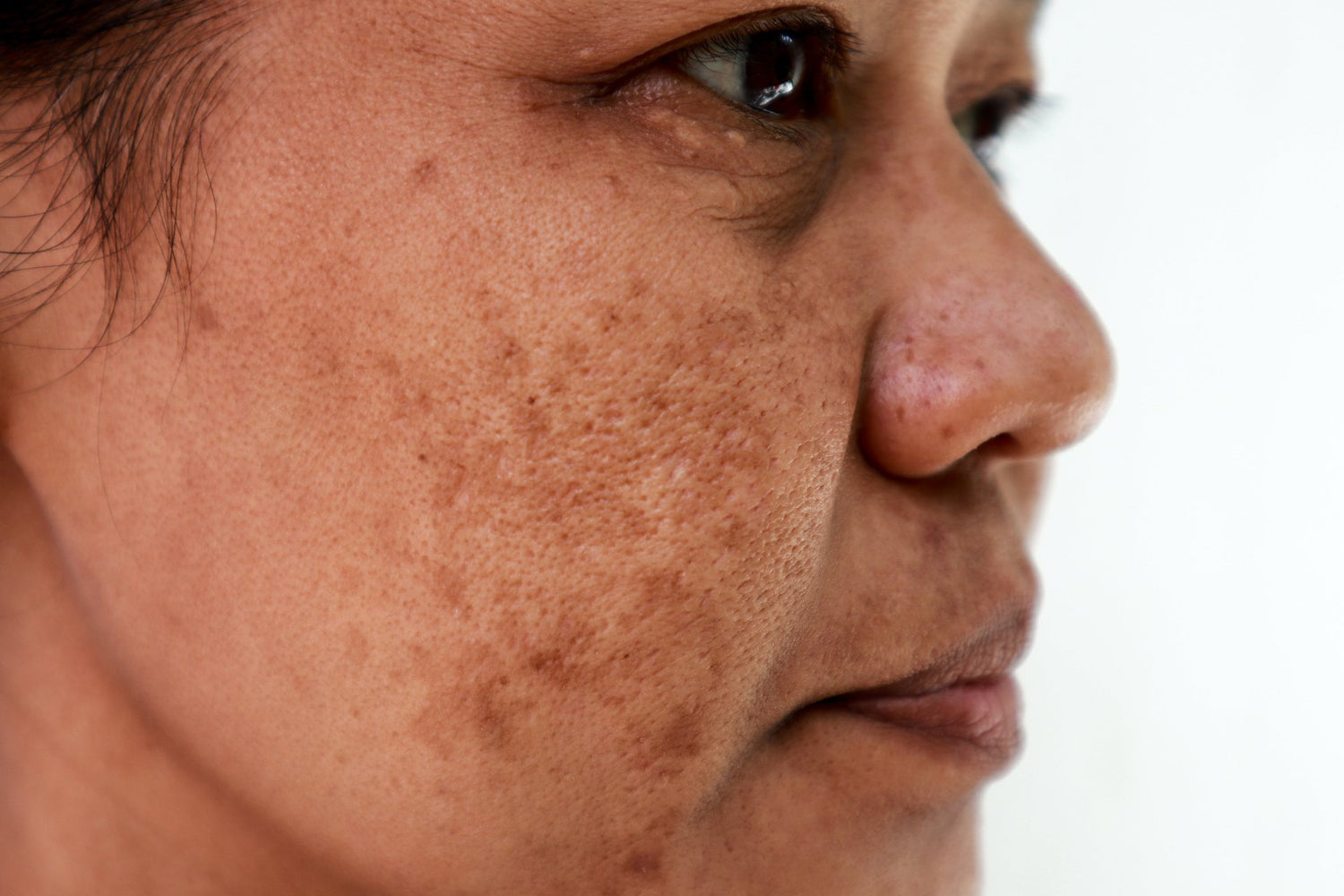
Broad-spectrum sunscreen refers to protection against both UVA and UVB radiation. UVB rays are mainly responsible for sunburn, while UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and contribute to long-term effects such as premature ageing and pigmentation. Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen helps reduce cumulative sun damage and supports healthier skin when used consistently as part of a daily routine.
Why is daily sun protection important?
Daily sun protection is important because the skin is exposed to ultraviolet and visible light not only during sunny weather, but also on those more cloudy days and through windows. This means that daily exposure is possible while driving or sitting indoors. Over time, repeated exposure can contribute to skin ageing, pigmentation and loss of elasticity. Applying sunscreen daily helps reduce the cumulative effects of daylight exposure and supports long-term skin health.
How does sun exposure damage the skin?
Sun exposure leads to the formation of free radicals in the skin, causing oxidative stress and cellular damage. This process can affect skin DNA, weaken the skin barrier and accelerate visible signs of ageing such as fine lines, uneven tone and reduced firmness. The effects are cumulative, meaning damage builds up over time, even with regular low-level exposure to sunlight.
Does sun damage occur even on cloudy days?
Yes. A significant proportion of ultraviolet radiation can still penetrate through cloud cover, meaning the skin remains exposed even on overcast days. UVA rays in particular are present year-round and can contribute to long-term skin damage. This is why daily sun protection is recommended regardless of weather conditions.
How can I protect my skin from daylight exposure year-round?
Protecting your skin from daylight exposure involves using a broad-spectrum sunscreen daily, alongside practical measures such as seeking shade and wearing protective clothing when appropriate. Sunscreen should be applied as part of your morning routine and reapplied during prolonged exposure. Consistent protection throughout the year helps reduce cumulative sun damage and supports healthier-looking skin over time.
Is sunscreen necessary indoors or in winter?
Sunscreen should still be used when indoors or during winter, as UVA rays are present throughout the year and can penetrate through windows. Although UVB exposure is lower in winter, cumulative UVA exposure can still contribute to skin ageing. Incorporating sunscreen into your daily routine helps provide consistent protection, regardless of season or environment.