Technologies to help correct hyperpigmentation
FAQs
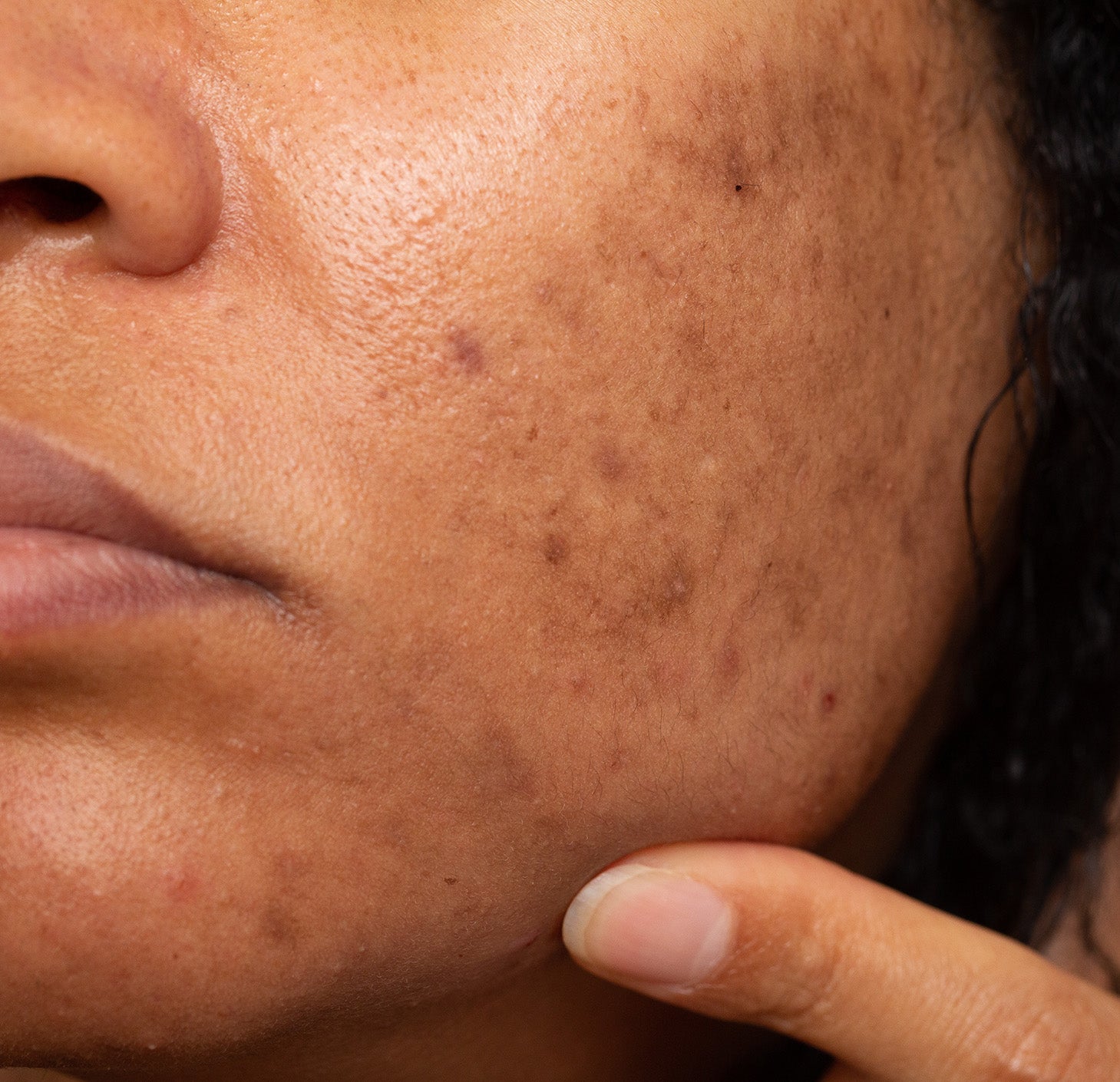
What causes hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation occurs when excess melanin is produced in certain areas of the skin, leading to dark patches or uneven tone. It can be triggered by factors such as sun exposure, hormonal changes, skin inflammation, acne, and ageing. The type and depth of pigmentation can vary, which is why hyperpigmentation may appear differently from person to person.
How long does hyperpigmentation take to fade?
The time it takes for hyperpigmentation to fade depends on the cause, depth of pigmentation and individual skin type. Some superficial pigmentation may improve within a few weeks, while deeper or more established pigmentation can take several months to fade. Consistent skincare and daily sun protection play an important role in supporting gradual improvement.
Can hyperpigmentation be prevented?
While not all hyperpigmentation can be prevented, the risk can be reduced by protecting the skin from known triggers. Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen helps limit sun-induced pigmentation, while gentle skincare can reduce inflammation that may lead to dark marks. Managing underlying skin concerns and maintaining a consistent routine can also help support more even skin tone over time.
Does sun exposure make pigmentation worse?
Yes. Sun exposure is one of the main factors that can worsen hyperpigmentation. Ultraviolet radiation stimulates melanin production, which can cause existing dark patches to deepen and new pigmentation to develop. This is why daily sun protection is considered essential when managing pigmentation concerns, even on cloudy days or during incidental exposure.
Is sunscreen important when treating hyperpigmentation?
Yes. Daily sunscreen use is essential when treating hyperpigmentation, as UV exposure can counteract the benefits of targeted skincare and increase the risk of dark marks returning. Using a high-level, broad-spectrum sunscreen such as HELIOCARE 360° Pigment Solution Fluid SPF50+ provides very high protection against UVA, UVB, visible light and infrared-A, helping to prevent pigmentation from worsening. Consistent daily sun protection supports treatment results and plays a key role in maintaining a more even skin tone over time.
Can skincare help reduce dark spots and uneven skin tone?
Targeted skincare can help reduce the appearance of dark spots and uneven skin tone by supporting skin renewal and improving overall clarity. Results depend on the type of pigmentation and consistency of use. Combining suitable skincare with daily sun protection helps create the best conditions for visible improvement and long-term maintenance of results.